Modals
A modal component can be used to respond to modal submissions. You’ll need to create and send these modals yourself, so let’s get started by creating a simple slash command to do so:
import { command } from 'jellycommands';import { TextInputBuilder, TextInputStyle, ModalBuilder, ActionRowBuilder,} from 'discord.js';
export default command({ name: 'test-modal', description: 'Shows a modal with a text input',
async run({ interaction }) { // Create a text input component with the builder const nameInput = new TextInputBuilder() .setCustomId('nameInput') .setLabel('Whats your name?') .setStyle(TextInputStyle.Short);
// All components need to be in a "row" const row = new ActionRowBuilder<TextInputBuilder>()).addComponents(nameInput);
// Create the actual modal const modal = new ModalBuilder() .setCustomId('test') .setTitle('Whats Your Name?') .addComponents(row);
// Send the modal interaction.showModal(modal); },});import { command } from 'jellycommands';import { TextInputBuilder, TextInputStyle, ModalBuilder, ActionRowBuilder,} from 'discord.js';
export default command({ name: 'test-modal', description: 'Shows a modal with a text input',
async run({ interaction }) { // Create a text input component with the builder const nameInput = new TextInputBuilder() .setCustomId('nameInput') .setLabel('Whats your name?') .setStyle(TextInputStyle.Short);
// All components need to be in a "row" const row = /** @type {ActionRowBuilder<TextInputBuilder>} */ ( new ActionRowBuilder() ).addComponents(nameInput);
// Create the actual modal const modal = new ModalBuilder() .setCustomId('test') .setTitle('Whats Your Name?') .addComponents(row);
// Send the modal interaction.showModal(modal); },});On running this command, your modal is opened! However, you’ll notice that when you submit the modal it fails:
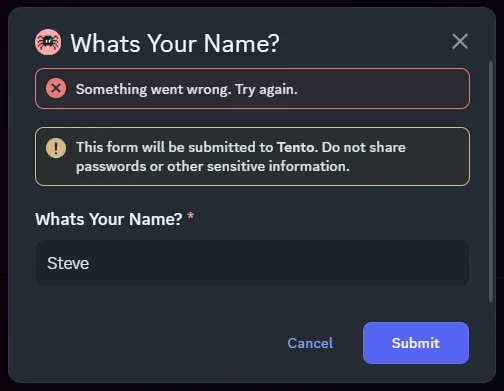
This is where the JellyCommands comes in, it allows us to create a modal component that can respond to these submissions. All we need is the modal’s “custom id”, which you might have noticed us setting in the above example. From here we can read the value of the text input using interaction.fields.getTextInputValue.
import { modal } from 'jellycommands';
export default modal({ id: 'test',
async run({ interaction }) { interaction.reply({ content: `Hello, ${interaction.fields.getTextInputValue('nameInput')}`, }); },});Now when we submit the modal we see that it sends our response!
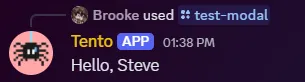
The “custom id” system is very powerful, allowing for dynamic matching to store arbitrary data. Learn more about custom ids.